IMPROVE is the fourth phase in the Six Sigma DMAIC cycle. The focus of this stage is to determine a solution which is based on the uncovered problem in the first three phases. This phase requires realization of the KPIV’s that are causing the outcome. The activity requires three things: (1) brainstorming by project owners and members whose goal is to create a solution that will address the main problem, (2) testing the solutions, and (3) assessing the outcome of the executed solutions. This stage will help conclude the amount and relationships of identified variables to the project Y. Most of the time before rolling-out a full-scale implementation, project owners conduct test run on a sample group. This is done to determine the finest settings. It is logical to choose the most effective setting which is also factored on the company’s resources, procedures and policies.
It is also essential to conduct a Stakeholder Analysis to make sure the group is ready to promote and encourage the change. Stakeholder Analysis is a chart that weighs the stakeholder’s position relative to the make over and commitment to the objective of the group.
Common tools used n this phase are the Seven Deadly Wastes, Five S, Benchmarking, and the Solution Selection Matrix.
The Seven Deadly Wastes corresponds to the areas that should be focused on when making an improvement. The areas considered in the Seven Deadly Wastes are:
- Overproduction – bottom line of this area is doing something that is unnecessary or not needed. Example creating several folders which comprises same files, making reports that is not relevant
- Time/Waiting – this can either be the job itself or the people involved in the job. Examples are: waiting for customer’s response, a transmittal, system loading.
- Defects – can be stated as repairs, rejects, or rework. These are jobs or parts that do not meet the customer’s requirements. Examples are: website or pricing error, inaccuracy in data entry, wrong information, and misplaced records.
- Process Inefficiency – ineffective procedure which results in poor outcome. Example is paperwork that passes thru several sections when it can just go with one or two sections, too much data gathering.
- Transportation – inefficient way of moving items or people. Example, taking documents to another employee for signature
Inventory – examples are offices stocks and supplies, open projects that are waiting to be worked on - Motion – excess movement may cause preventable fatigue and sometimes long term injury. Preparation for work, gathering of information, and clearing away documents on desk are some examples of this area.
Implementation is the focus of Improve phase. Some project owners use the concept of Five S to create visual control on the work place. This methodology aims to improved safety, quality, and efficiency. The effect therefore is reduced cost and waste, and improved management.
The approach is called the Five S because of a very plain idea. All five actions start with a letter S.
- Sort – is performed by determining the unneeded things and transferring them to an impermanent holding place. Decision has to be made as to either to keep or retain an object or a process. Within a given period of timeline, these objects can be disposed, given away, or sold.
- Set in Order – spot the preeminent location for the remaining objects, rearrange items that are out of place, place inventory limits, and put in impermanent position indicators.
- Shine – clean everything in the interior and exterior. Keep on to inspecting items by cleaning them also to prevent dust, dirt, and contamination from happening.
- Standardize – rules should be created to keep and control the first three Ss. This also can be done thru the use of graphic controls.
- Sustain – guarantee adherence of the five Ss standards through messaging, instructions, and discipline.
Benchmarking is another tool that can be used during the Improve phase. This is a procedure used to calculate various characteristics of a certain process in relation to the most excellent practice. This permits the group to develop strategies on how to implement such best practice, typically with the intention of increasing some characteristics of performance.
Benchmarking vary on types:
- Process benchmarking – using the identified best practice of one or more benchmark firm as reference, the instigating firm centers its interpretations and examinations on business processes. Analysis on the activity will be required where the goal is to scale efficiency and cost.
- Financial benchmarking – conducting an economic analysis and matching it up with the results in a effort to evaluate the general competitiveness
- Performance benchmarking – matching of product and service versus the product and service of the competitor’s company
- Product benchmarking – identifying the strengths and weaknesses of a certain product or service for the purpose of creating a new product or offering a new service
- Strategic benchmarking – engages in observing how other market players compete. This type is not particular in one specific company but looks at the filed in a bigger perspective.
- Functional benchmarking – a business will center its benchmarking on a sole function for the purpose of improving the business or process of that particular task.
The Solution Selection Matrix is another tool material to Improve phase. This tool allows project owners to review the knowledge regarding the process and its cause verified. The activity includes brainstorming of possible solutions and combining those solutions into one main process. In order to achieve better solutions, three simple steps should be followed. Generate criteria, weight criteria, and evaluate criteria.
The table below will illustrate the use of the Solution Selection Matrix. Criteria and weights are plotted to determine impact and value to the organization. Project members will vote and these votes will be multiplied to the corresponding weights. The solution which earned the highest votes will most probably be implemented.
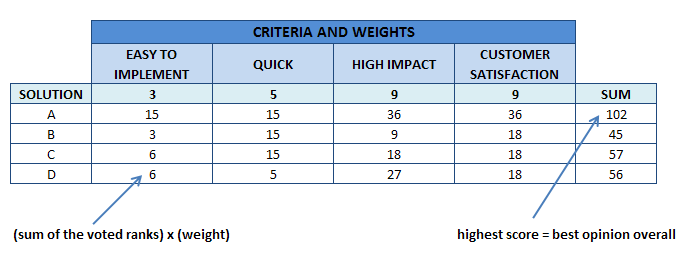
Solution Selection Matrix
Since this phase requires several activities and monitoring, another valuable tool to use is the Gantt chart. This shows the start and the end dates of each activity. Best used to track and monitor assignments.
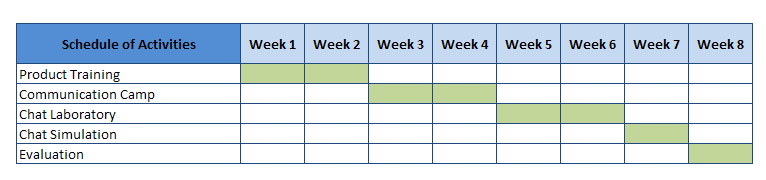
Gantt chart
Solutions that are created in this phase are based on the gathered data and thorough analysis. It is safe to say that this phase will attest if the analysis done in the first three stages is correct.
