Total Productive Maintenance is a process/concept by which an organization can optimize the production capability and quality, by effectively managing and maintaining the machines, equipments, operators and the related processes.
The name is similar to Total Quality Management, but they are not synonymous. TQM is an approach to improve the Quality of the products/service delivered by an organization. It utilizes concepts like Six Sigma, LEAN, Zero Defects, Process Reengineering and Improvement, KAIZEN and many others to improve the Quality, Customer Satisfaction, operational efficiency and reduce cost & defects. TPM is actually a sub set of tools for achieving a Quality Product/Service, Process Excellence, Reduced operational cost, customer satisfaction.
The main objectives of TPM are:
- Increase the productivity of the plant
- Reduce breakdowns & minor stoppages
- Avoid Defects and defective items
- Minimize and optimize set-up and change over time
- Create a Safe work environment
The TPM Model
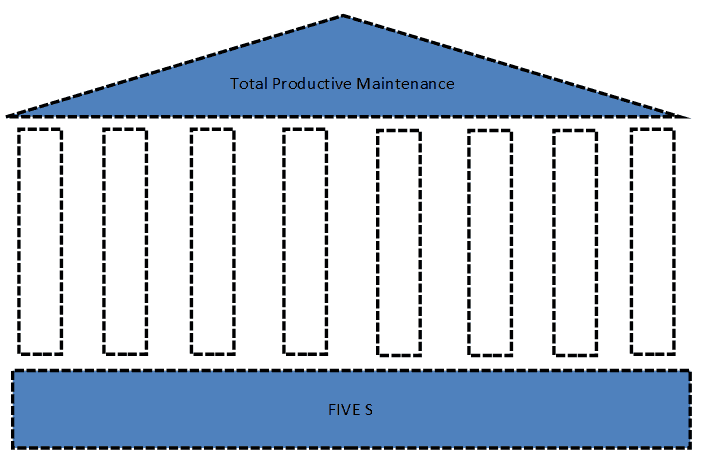
The foundation of TPM model is the most simple and essential concept: ‘Five S’ which focuses on work space management.
Eight pillars form and lead to implementing and sustaining Total Productive Maintenance:
- Autonomous Maintenance: Enabling and empowering the operators and for routine maintenance, inspection and minor repairs.
- Planned Maintenance: Schedule maintenance timings and frequency based on historical and predicted data on failure.
- Quality Maintenance: Design processes and enable equipments and operators to detect and prevent errors at the earliest stage.
- KAIZEN: Having a small workforce engaged in identifying opportunities in improving the system
- Early Equipment Management: Understand and design custom equipments that are aimed to achieve TPM
- Training: Training the workforce and creating a knowledge base on known errors and repair processes
- Safety, Health & Environment: Make Safety and employee health a core part of maintenance and process design
- Implement TPM in Support Functions: To make it a culture across the organization and employees to be aware of the need and benefits of TPM.
Thus TPM aims to improve the efficiency of the production system through proper design and maintenance of the equipments and machineries involved. It is extremely useful in factories, manufacturing and production units and wherever machineries are used, whatever are the type, size and value of it.
