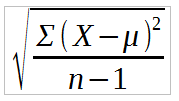Machine capability index is an index derived from the observations from uninterrupted/continuous production run. It is often known as Cmk. It is a short-term capability index and also called initial process capability. The long-term capability index can be calculated for a machine/process after achieving the required Cmk value.
A machine capability study is the testing of a machine in regards to its suitability for a special production task. Machine capability index can be used to measure the effectiveness of process improvement efforts. It is used to study the position of the machine’s capability in relation to the tolerance limits. It describes the capability corrected for position.
The formula to calculate Cmk is same as Cpk, but the standard deviation used here is sample standard deviation. But, for Cpk standard deviation is measured from the control chart, as this is a measure of process performance. Cmk is measured using continuous samples keeping all influences other than the machine parameters constant. Stability is verified by plotting this on control chart to look at whether the process is stable.
Interpreting Cmk
Cmk = min 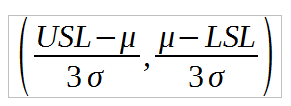 , where s is the standard deviation of samples
, where s is the standard deviation of samples
For instance, Machine A has Cmk of 1.5 and Machine B has Cmk of 1.87. Machine B is a better machine. Here a high Cmk index means that you have a good machine with a small spread in relation to the tolerance width, and also that it is well centered within that width. However, if machine has larger average deviation then it accounts for higher possible defects while in production.
A normal or preferred requirement is that Cmk should be at least 1.67. A Cmk value of 1.67 testifies that 99,99994 percent of the assemblies are within the allowable tolerances. This means that the fault rate is 0.6 per million. If Cmk is equal to Cm, the machine is set to produce exactly in the middle of the tolerance range.
Where, Cm is the index that describes machine capability. It is the number of times the spread of the machine fits into the tolerance width. If Cm= 2.5, the spread fits two and half times into the tolerance width and if Cm = 1 then spread is equal to the tolerance width.
A machine capability study concentrates exclusively on the characteristics of the machine. To the extent possible the influence or effects of variables external to the machine are minimized. Keeping other influences constant, it is expected that only machine’s inherent sources of variation will affect the product and its characteristics. In cases where this is not possible, the changes in the external influencing factors should be record the test results. This information can further be used for optimization in case capability specifications don’t meet.