‘Five S’ is one of the names that most of the people in manufacturing industry, and those in Quality & Operations management would have come across mainly in their career. It is one of the tools and techniques used as a part of LEAN, JIT (Just-In Time Manufacturing), and many other operational excellence methods. The base of 5S lies in work place management and there by contribution to reduced processing time/ cost and thus achieving LEAN or Just-In-Time Production. The method has its origin from Japanese manufacturing companies who are known for their orderliness and perfection.
Why should I use 5S?
Because it is a simple and logical method with no technicalities involved, but has loads of visible and tangible benefits. Some of them are:
- You can easily identify and store your items/parts/files in a 5S workplace
- It standardizes the location/position of items/parts and hence simplifies the job of a processor or team member involved in the job.
- It removes unwanted items and files and thus keeps the workplace clean and simple.
- It brings hygiene and cleanliness to the workplace and thus provides confidence and receives appreciation from external stakeholders.
How do I perform a 5S Operation?
As the name indicates 5S has five levels or steps that should be performed sequentially and cyclically. They are:
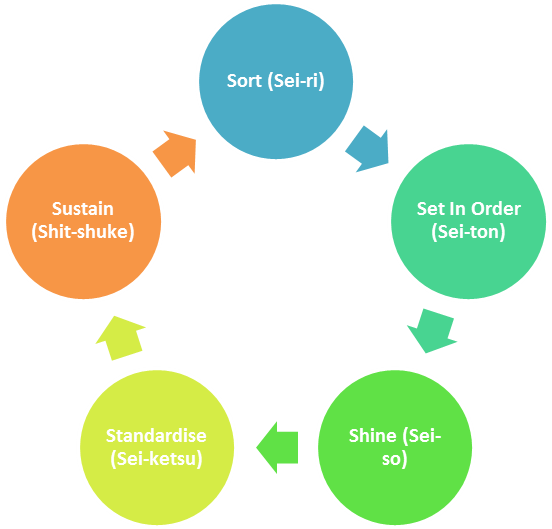
1S: Sort (Sei-ri):
Remove the unwanted/unnecessary/unused/obsolete parts/items/files and other objects in the workplace. This might include archiving and deleting obsolete and irrelevant files/folders in your computer. So, 5S can be used even for IT and ITES, back office and other Office based workplaces, if the key concepts behind the method is properly understood and customized to the workspace.
2S: Set In Order (Sei-ton)
Once the unwanted stuff is cleared, the next step is to organize and arrange the exiting items in a neat and easily accessible manner. This step makes the processers life easy by helping him to spend more of his time in productive tasks and not wasting time in searching for items/objects.
3S: Shine (Sei-so)
After the items are kept in order, the entire workplace should be cleaned to give a neat and fresh appearance. This brings a sense of motivation and enthusiasm to employees who use the workplace. It also helps to maintain safety and hygiene in the workplace.
4S: Standardise (Sei-ketsu)
The next step is to bring to routine practice the above three steps. Rule, ownership and frequency of each step for repetition should be defined based on the workplace area and the nature of work that is being carried out.
5S: Sustain (Shit-shuke)
The final and important step is to sustain the changes and improvements brought thorough implementation of 5S. The management should identify ways like having documents in place for 5S steps, scheduling audits in surprise, recognising and rewarding teams for sustained 5S work place etc.
Thus an organisation can achieve excellence by moving up in the ladder of 5S, which is a low-hanging fruit for many organisations.
